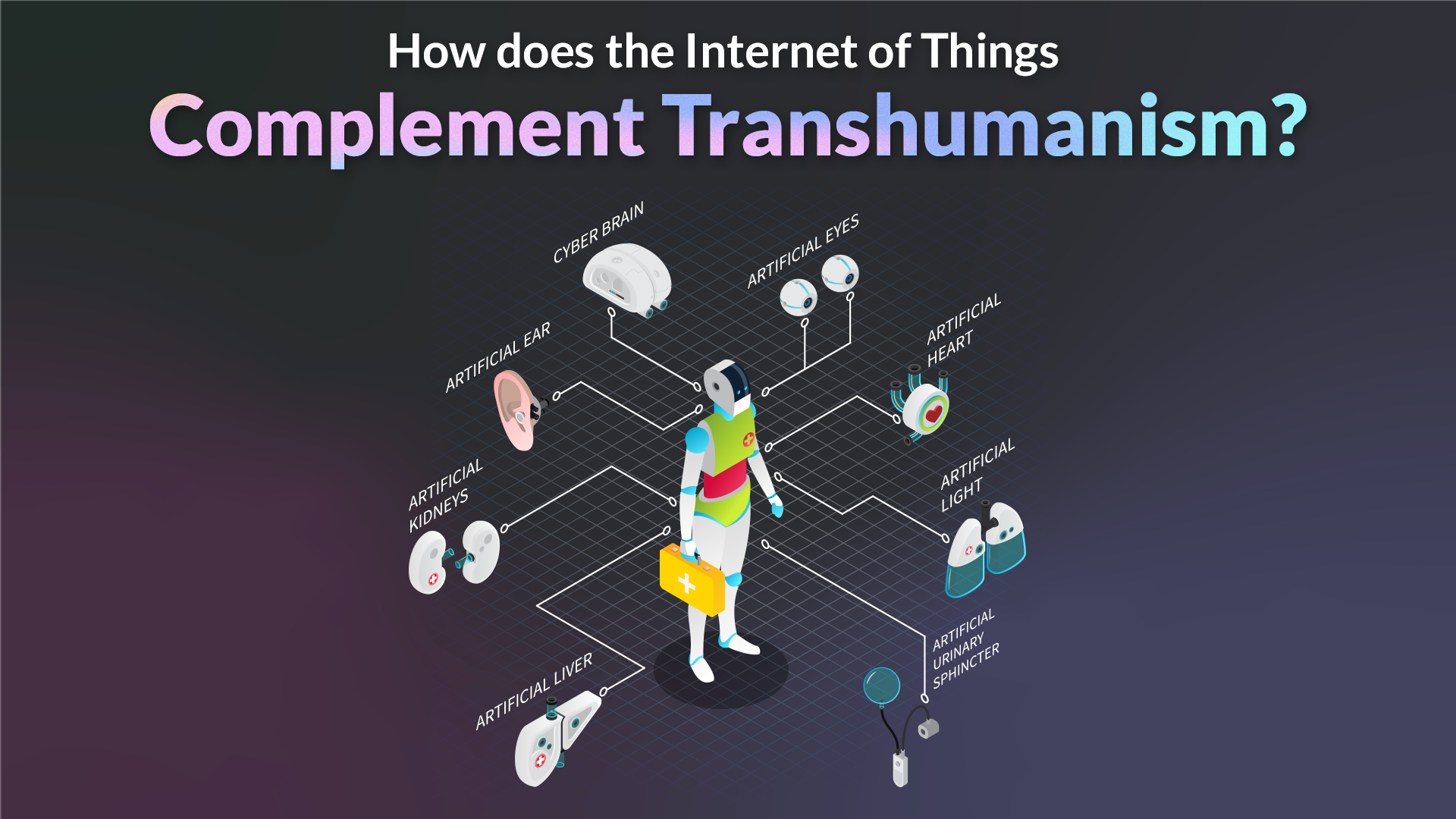
The debate around Transhumanism has seen quite a lot of resurgence following the commercialization of technologies like CRISPR. The idea of advancing the human race artificially has been a point of much debate around various institutes worldwide. It’s no surprise, and nobody would like to think of a future with real-life superhumans with their technologically enhanced superhuman abilities.
Although that future is far off, the use of technology to improve and enhance people with disabilities and ailments has seen very enthusiastic adoption and acceptance, From artificial limbs, artificial skin, and even organs, the ground reality of human life is changing slowly, and with the need to have everything connected, IoT has been one industry that has become the backbone of all this technological evolution.
We also know that the rapid advent of technology will change how humans behave. Most big companies invest in various technologies like the internet of things, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. We also know that this transformation will be messy and scary, out of the box. Still, the present already shows how our real identity will be condensed into transhumanism by using the internet of things. So, let’s move into the blog and understand how the internet of things will change the human body and behavior in the future and the outcome of such change.
3 Ways in which IoT is changing the Human Body
Everything consists of connectivity, the internet, and automation. Even the movies we enjoy show the concept of the internet of things. If you watched the Bollywood movie WAR, you must have seen small chips embedded inside the filmmakers’ bodies as monitoring sensors for defense applications. These chips are classic examples of IoT devices in the human body. Let us see how IoT is changing the human body.
Digital Pills
Sensors and cameras embedded in tiny edible devices are used in this novel form of medicine delivery. By letting clinicians monitor their patients’ biological functions in real-time, such medical gadgets improve diagnoses, monitoring, and treatment of life-threatening medical disorders. Furthermore, because this technology can send medication to particular portions of the body, it removes many of the adverse effects of traditional drug delivery.
Recent experiments done by MIT researchers might prove these devices to be a savior for many cancer patients. Patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer in stages 3 or 4 are eligible for this program. Instead of taking their standard chemotherapy prescription, the patients are given a sensor-embedded version of the identical medication that alerts the doctor when it is consumed. The sensor will activate once the pill is ingested and send a signal to a patch worn on the patient’s body. The data will subsequently be sent to an online portal via the patch. The information will include the time of day the medication was taken, the type of drug, and the dose size.
RFID Microchips
RFID can help healthcare providers achieve new efficiencies and improve their offerings. RFID can help hospitals and medical facilities gain a competitive advantage by streamlining workflows, increasing production, lowering operating costs, and improving patient care. In addition, patient identification confusion, medication mishaps, and pricey mobile medical equipment theft could all be prevented with RFID.
IoT-enabled RFID tags are combined with wireless microsensors to monitor and store ECG, pulse rate, basal temperature, and other vital signs of patients noninvasively, then communicate them to the care providers’ database at predetermined intervals.
Smart Contact Lens
Smart contact lenses are similar to implants in that they do not require surgery and may typically be withdrawn or placed by the user. However, they’re not on or under the skin all of the time. Instead, they’re exposed to both air and the human body’s chemistry. They can capture energy by being exposed to both light and the mechanical activity of blinking. These lenses also monitor health diagnostics like glucose levels based on the eye and ocular fluid information. This allows diabetic people to monitor glucose levels in their bodies without having to repeat pin-pricks throughout the day.
Conclusion
We see how the Internet of things changes human lives by becoming one part of it. There are several advantages of IoT equipped with a few disadvantages. After Covid 19, the internal infrastructure of treatment and medical emergencies has changed, giving rise to more automated services. IoT will be the talk of the town for the future healthcare sector. We cannot ignore the role of IoT in bringing the future of humans!