Counting your daily steps on your smartwatch after a workout, or asking Alexa to change the song while having a relaxing bath, almost every technological comfort that we seem to take for granted is a part of the Internet of Things. The gadgets we connect over a network operate on the internet of things principle in less than a second. IoT, in simple terms, means the internet controlling things over a range of networks. The applications of IoT are widely used in various industries to manage and simplify processes, which results in higher output.
Nevertheless, smart farming and crop monitoring using IoT have been a hot topic filling the market since its inception. Farming is becoming more industrialized and tech-driven by adapting several technological transformations in the last decade. While drones are used for imaging and mapping the farms, agricultural organizations are investing in using remote sensing and robotics for crop monitoring and harvesting. In this article, we will talk about the benefits and applications of using IoT in agriculture and how it is helping businesses to grow the market worldwide.
If you’ve ever considered investing in intelligent farming and crop monitoring or plan to build an IoT solution for four farms, dive right into our blog.
What is Smart Farming? The Meaning and the Market Size.
Smart farming is the 21st century equivalent of the age-old traditional farming practiced since time immemorial. There are many notions for introducing smart farming in today’s tech-driven world. For example, Agritech refers to the application of technology in agriculture.
Similarly, smart farming is used to denote the application of IoT solutions in agriculture. So what is smart farming using IoT? By using IoT sensors and drones to monitor the environmental effects and soil conditioning, farmers can make informed decisions and improve their working conditions.
Although the agriculture IoT and Industrial IoT markets are very dynamic, the adoption of IoT solutions in the market is growing. COVID-19 has had a significant impact on the agriculture market share. A shortage of qualified workers and disruption in the supply chain has propelled its CAGR to 9.9%. As a result, the smart farming industry will reach $6.2 billion by 2021, and the global market size is expected to triple by 2025.
As you can see, the agriculture IoT market is still developing; there is a higher scope of opportunities for businesses to grow and invest in it. But, most importantly, building the IoT products for agriculture in the future scenario will prove beneficial and set you apart as the early adopter to pave the way to success.
Benefits of using IoT Solutions in Farming and Crop Monitoring
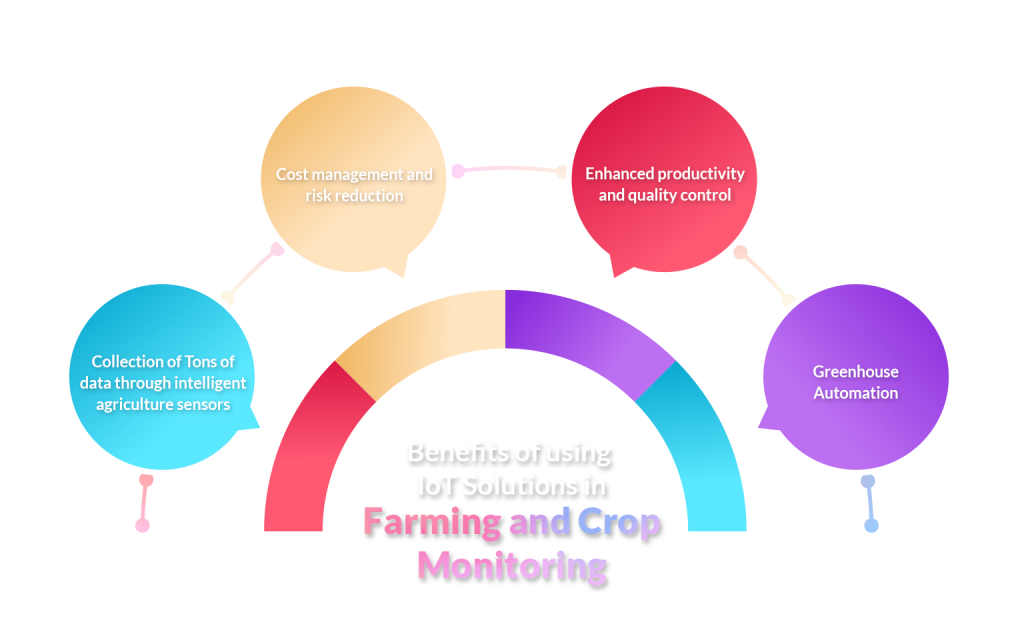
The Internet of things has multiple and over-the-top benefits in agriculture. Meanwhile, it also has the potential to diminish the recurring agricultural issues. So let’s find out how IoT is beneficial for the agriculture industry.
- Collection of Tons of data through intelligent agriculture sensors: The agricultural farms have a lot of data that goes into vain because there is no availability for data processing. However, after installing IoT sensors, you can monitor and collect data for soil quality, weather conditions, crop growth progress, etc. This data will help analyze the growth of the business in general as well as staff performance, equipment efficiency, etc.
- Cost management and risk reduction: Once you start analyzing the data and costs of the production, it is likely that if any anomalies occur in the crop or farm, you will be able to mitigate the risks and work accordingly for yield safety.
- Enhanced productivity and quality control: IoT-based equipment help maintain productivity and achieve better control over the production process to maintain crop health and growth capacity through automation.
- Greenhouse Automation: Typically, producers control the greenhouse atmosphere through manual intervention. They may acquire accurate real-time information on greenhouse parameters, including illumination, temperature, soil condition, and humidity, by using IoT sensors.
Case Study: The appearance of IoT based Smart Farming in Brazil

Recently, Telit, internet of things company, has joined hands with Brazilian non-profit ConectarAGRO to develop and distribute intelligent farming solutions to the Brazilian farmers to increase yield and productivity across the country.
Despite many technical advancements, connectivity remains one of the most significant challenges Brazilian farmers face today. The reports show that only 23% of the nation’s agricultural sector has access to internet connectivity, significantly less than the other countries.
This collaboration will bring most of the country’s farms online using several IoT-enabled devices. Under this collab, Telit’s pipeline and IoT-based monitoring systems will be used to analyze the data from different fields and work on it to produce safe crop production, irrigation management, livestock, precision farming, and regulatory compliance. In addition, this initiative will break the gap between customers and suppliers, enabling a digital and fast delivery system throughout the country.
“Agriculture IoT application developers and system integrators have a unique chance to design connected farming products that increase yields, lower costs, and a well-fed world,” Fernando Guerra, Telit’s Latin American regional sales director, stated.
According to ConectarAGRO, the company used 4G to connect more than 12.6 million acres of rural land in Brazil in 2019, reaching 575,000 people in 218 municipalities across eight states. The organization wants to expand this achievement throughout Brazil during its lifetime.
Challenges faced by Businesses while Creating IoT Platform
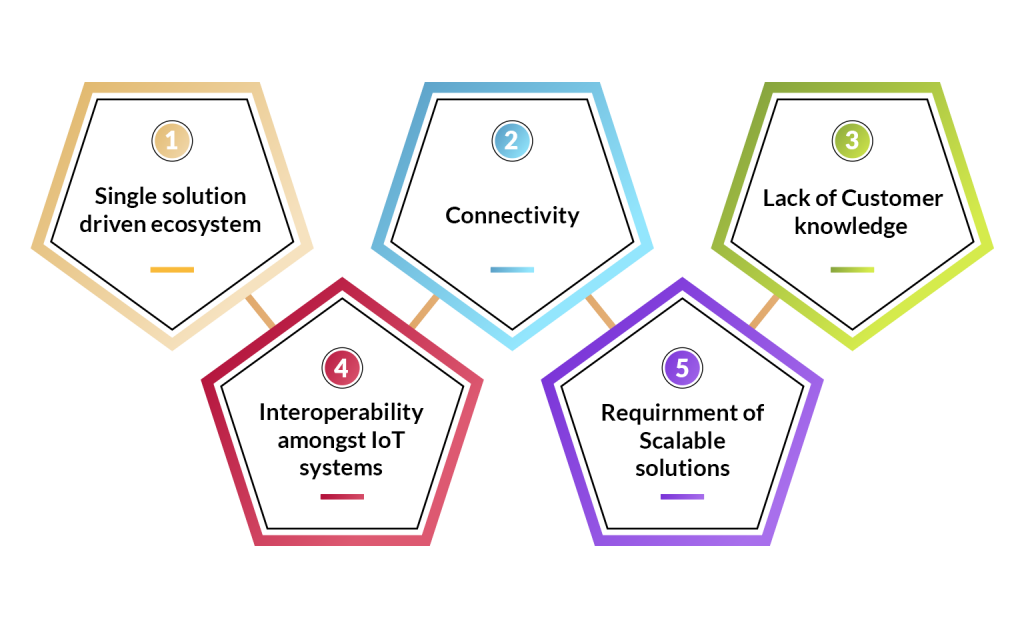
IoT plays a master role while helping the agriculture sector boom in the coming years. However, there are specific challenges that every business faces while creating automated solutions for the consumers.
- A single solution cannot be used with different IoT devices, i.e., device ecosystems are highly closed and commonly limited to the provider’s proprietary hardware.
- Connectivity is the most common difficulty for the Internet of Things in agriculture. Every location lacks adequate internet access.
- The lack of customer knowledge is the second most common barrier to IoT-based Smart Farming.
- Interoperability across different IoT systems becomes extremely tough due to various service providers.
- A scalable solution can be combined with thousands of IoT devices for large farms.
Conclusion
Internet of things has spread over a decade of advancements and applied these changes in the agriculture industry. IoT devices include every minute object that can be controlled by internet connectivity. It has become commonplace in the consumer market with the emergence of intelligent wearables, tools, sensors, and devices.
The Internet of Things applications in agriculture aims at traditional farming operations to fulfill rising demand and reduce production losses. Robots, drones, remote sensors, computer imagery, and ever-improving machine learning and analytical tools are used in agriculture to monitor crops, survey and map fields, and deliver data to farmers for sensible farm management strategies that save time and money.